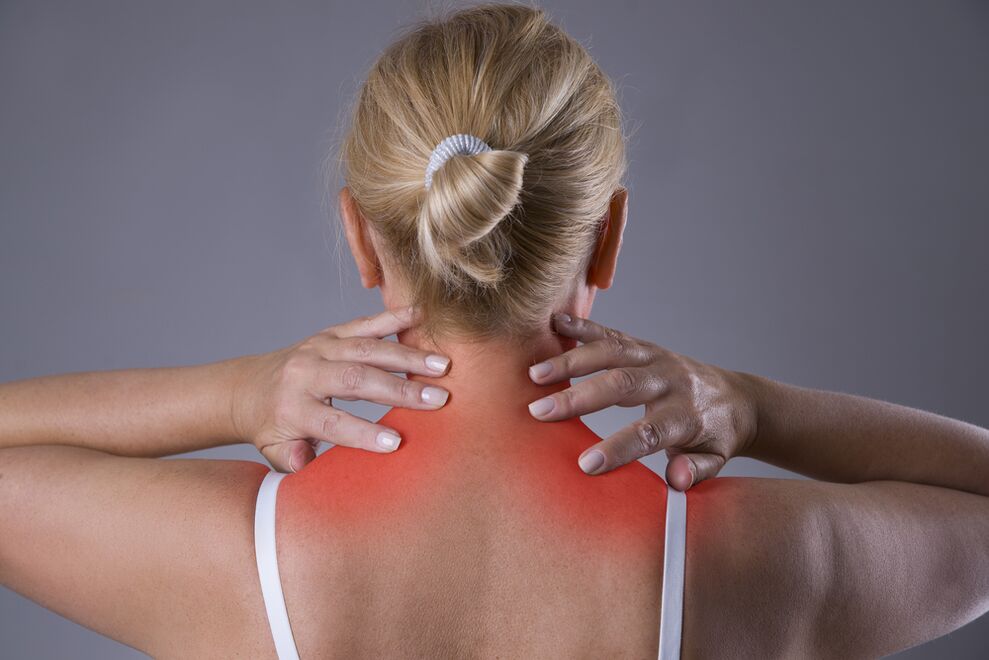
It is important to recognize the first signs of cervical osteochondrosis in time to seek qualified medical help and prevent the negative consequences of the disease: chronic hypertension, heart attack, stroke, partial or complete limitation of motor activity, disability.
Why is osteochondrosis dangerous?
The main function of the intervertebral discs is to cushion and prevent any damage to the vertebrae when walking, running and jumping. In addition, they ensure the mobility of the entire spine.
As the body ages naturally and due to the influence of unfavorable factors (stress, injuries, excessive physical activity), the height of the intervertebral discs decreases. The progression of osteochondrosis causes the following complications:
- The dense fibrous ring of the intervertebral discs is destroyed and cracks appear in it.
- The contours of the intervertebral disc are displaced beyond the physiological limits, forming a protrusion.
- Without the help of specialists in the previous stages, the patient faces a rupture of the annulus fibrosus and a hernia.
- Osteophytes form in cartilage and bone tissue, pathological growths that become one of the causes of decreased mobility and pain in the spine.
- The roots of the spinal cord and surrounding tissues are subject to compression and inflammation.
Characteristics of cervical osteochondrosis that are not talked about.
Many people mistakenly believe that osteochondrosis is exclusively an age-related disease. But, in most cases, osteochondrosis of the cervical spine begins to develop in childhood as a result of birth trauma. For many children, the first clear symptoms appear when they start school. It is during this period that the need to sit for a long time in a forced position, physical inactivity and spasms of the neck muscles as a reaction to stress are added to the already existing negative phenomena and factors.
Many birth injuries of the cervical spine are not noticed during normal visual examination. Although it is because of them that children, and later adults, experience serious problems with the respiratory, cardiac, central nervous system, sensory and motor functions of the body.
What threatens the development of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine?
The brain is responsible for regulating the entire body. It is also the main consumer of oxygen, which arrives through the blood.
Blood supply to the brain is provided by the basilar artery. This, in turn, is formed from the fusion of two vertebral arteries that pass through the cervical vertebrae.
Deformation and damage to the intervertebral discs causes instability and displacement of the cervical vertebrae. Compression of one or both vertebral arteries occurs, as a result of which the oxygen supply to the brain is reduced and it begins to send orders to increase pressure. This is how chronic non-infectious diseases develop, in particular hypertension.
Over time, patients experience alterations in the functioning of the cardiovascular system. The risk of stroke, heart attack and coronary heart disease increases significantly. In men - impotence.
Symptoms of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine.
- Spasm and limitation of neck mobility, pain when turning and tilting the head.
- Burning, pain, feeling of a lump in the throat, difficulty swallowing.
- Numbness and coldness of the hands or just the fingers.
- Pain and burning in the chest.
- Shortness of breath
- Chronic hypertension
- Headache, migraine
- Dizziness, fainting
- Noise and ringing in the ears.
- Decreased visual acuity, appearance of spots before the eyes.
- Increased fatigue, weakness, drowsiness, decreased performance.
- Difficulty concentrating, forgetfulness.
- Sleep disorders
- chronic depression
- Panic attacks
- Pain of varying intensity, spreading to the neck, shoulders, collarbones, upper back and the entire surface of the head from the back of the head to the forehead.
If you notice any of the listed symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis of the spine, we recommend that you immediately contact specialists in a modern clinic. Professional doctors will carry out comprehensive diagnoses and develop individual treatment procedures.
Treatment of cervical osteochondrosis in men and women in the clinic.
The technique patented by the candidate of medical sciences, Dr. Alexander Yuryevich Shishonin, makes it possible to stop the development of osteochondrosis and significantly improve the well-being of patients of all ages.
At the initial appointment, the clinic's specialists perform a microanatomical ultrasound of the vessels of the neck to measure the speed of blood flow and identify muscle spasms that cause compression of the vertebral arteries.
Treatment of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine includes:
Physical therapy. Physical inactivity is one of the key reasons for the development of osteochondrosis. Therefore, an individual set of physical exercises is developed for each patient. A complex of exercise therapy is prescribed depending on the diagnosis, the patient's health status and the presence of acute or chronic diseases.
All exercises are performed under the supervision of certified instructors on special simulators, which helps to restore muscle tone and strengthen the muscle corset.
Correction of the deep muscles of the neck and back.. The clinic's correctors restore blood supply to the brain by manually manipulating the deep muscles of the neck and vertebrae. Blood pressure normalizes, cognitive functions (memory, concentration, mental performance) improve.
You can learn more about the wide range of services and all the features of osteochondrosis treatment in a professional clinic by reading more detailed materials.
Prevention of the development of cervical osteochondrosis.
You can prevent the appearance or development of the disease by following the following recommendations:
- Take long daily walks. In total, it is necessary to take at least 6, 000 steps a day.
- Do sport. The load should not be excessive. Start with doable exercises, gradually increasing the duration of the exercise and the number of repetitions.
- Balance your diet and maintain a normal body weight.
- Perform Dr. Shishonin's neck exercises.